Datasheet 搜索 > AD转换器 > Maxim Integrated(美信) > MAX186DCPP+ 数据手册 > MAX186DCPP+ 开发手册 1/7 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 258.013
MAX186DCPP+ 开发手册 - Maxim Integrated(美信)
制造商:
Maxim Integrated(美信)
分类:
AD转换器
封装:
DIP-20
描述:
MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS MAX186DCPP+. 模数转换器, 12 bit, 133 kSPS, 双 (+/-), -4.75 V, 5.25 V, DIP
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
MAX186DCPP+数据手册
Page:
of 7 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > A/D and D/A Conversion/Sampling Circuits > APP 1108
Keywords: single-ended, signal conditioning, pseudo differential, fully differential, common mode rejection,
CMRR, noise, ADC, a/d, analog digital, analog to digital, converters, convertors
APPLICATION NOTE 1108
Understanding Single-Ended, Pseudo-Differential
and Fully-Differential ADC Inputs
Jun 14, 2002
Abstract: Many of today's instrumentation and process control applications convert the analog output of a
sensor for processing and/or storage using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). For voltage input ADCs,
three different input structure types exist: Single-Ended, Pseudo-Differential and Fully-Differential. This
tutorial explains the differences, advantages and tradeoffs between the input types.
Many of today's electronic instruments rely on microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs) to
process real world, analog signals. Sensors convert a natural parameter, such as temperature or
pressure, into a voltage or current. Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs, or A/D converters) convert the
signal into digital form.
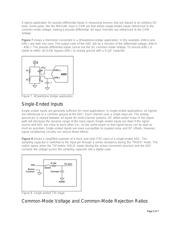
For voltage input ADCs, three different input structure types exist: Single-Ended, Pseudo-Differential and
Fully-Differential.
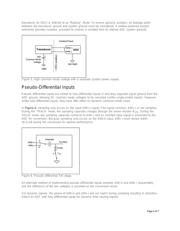
The simplest solution is to select an ADC input structure that matches the sensor output. However, there
are trade-offs with each structure that should be considered. In addition, if signal-conditioning circuitry is
used between the sensor and the ADC, this circuitry can affect the ADC input structure choice. Some
ADCs are configurable, allowing selection between single-ended or pseudo-differential input structures
(MAX186, MAX147) while others allow a choice between single-ended or fully-differential (MAX1298,
MAX1286).
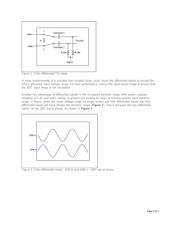
Fully-Differential Inputs
For maximum noise rejection, use fully-differential inputs. Figure 1 shows an example of a fully-
differential ADC T/H input structure. During track mode, Csample(+) charges to [AIN(+) Ð V
DD
/2] and
Csample(-) charges to [AIN(-) Ð V
DD
/2]. When the T/H switches to hold mode, Csample(+) and
Csample(-) connect together in series, such that the voltage sample presented to the ADC is the
difference of AIN(+) and AIN(-). The differential architecture in conjunction with acceptable input bandwidth
in the T/H are key ingredients for good dynamic common-mode rejection.
Page 1 of 7
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件