Datasheet 搜索 > 接口芯片 > Maxim Integrated(美信) > MAX3232CSE+ 数据手册 > MAX3232CSE+ 开发手册 3/9 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 5.575
MAX3232CSE+ 开发手册 - Maxim Integrated(美信)
制造商:
Maxim Integrated(美信)
分类:
接口芯片
封装:
SOIC-16
描述:
MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS MAX3232CSE+. 收发器, RS232, 2驱动器, 3V-5.5电源, SOIC-16
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
MAX3232CSE+数据手册
Page:
of 9 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
3V transceivers, which feature a low quiescent current, the capability to drive a mouse, a low-power
standby mode in which some (or all) receivers are active, a flow-through pinout, and operation to
230kbaud (to support high-speed modems).
Unique Output Stage Uses 50% Less Power
Maxim's key innovation in developing 3V parts is a driver output structure with very low voltage drop from
input to output. Low voltage drop is important because the ideal DC/DC converter for 3.3V RS-232
transceivers is a capacitive voltage doubler. A perfect doubler would produce 6V for 3V minimum inputs,
leaving a drop of just 1V for losses in the driver output stage and the DC/DC converter itself.
Moreover, the output swing for an ideal RS-232 transceiver would be ±5V with a tolerance of zero. A
minimum of ±5V is needed to comply with the RS-232 specification, but any swing above 5V or below -5V
simply wastes power. Regardless of input voltage, therefore, members of the MAX3241 family regulate
their internal, voltage-doubling DC/DC converter to 5.4V—just enough to provide a safety margin after
covering the 200mV drop in the driver output stage. The result is minimal power consumption at the
nominal 3.3V supply rail.
An ideal (lossless) capacitive voltage doubler, unregulated, produces 6.6V with a 3.3V input and 10V with a
5V input. Thus, an RS-232 transceiver with internal 5V doubler wastes the 5V difference between its
output (10V) and the desired ±5V as specified by the RS-232 standard. An internal 3.3V doubler, which
wastes only 1.6V, is therefore much more efficient.
Similarly, an ideal 3.3V capacitive tripler generates 9.9V. The desired output is 5V, so the overall efficiency
is only 5/9.9 (51%). Another way to compare the 3.3V doubler with the 3.3V tripler is to note that, for every
1mA drawn by the RS-232 load, the doubler draws 2mA (from the 3.3V supply) while the tripler must draw
3mA. Thus, the power saved by a 3.3V doubler is even greater when driving the capacitive load of a long
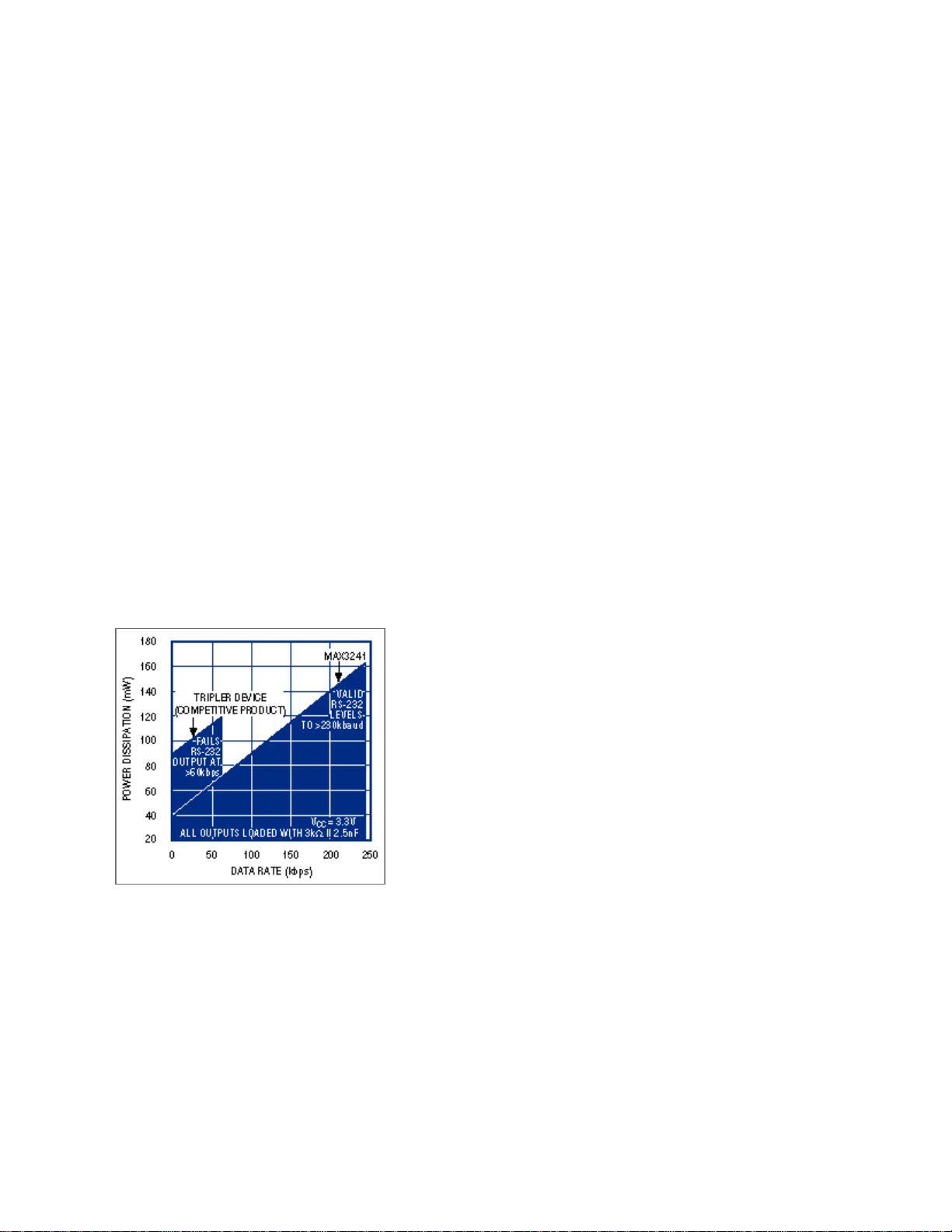
RS-232 cable at high speed (Figure 1).
Figure 1. The MAX3241 (with voltage doubler) consumes only half as much as power as does the
competitive device based on a voltage tripler. Note also, the MAX3241 maintains valid RS-232 output
levels at quadruple the data rate.
RS-232 drivers must also supply output current for driving the input resistance (3kΩ to 7kΩ) associated
with the RS-232 receiver at the far end of the line, and for charging and discharging the load capacitance
(up to 2.5nF, as specified by the RS-232 standard). This charge/discharge current increases with
frequency, and exceeds the resistive current at a data rate of 80k bits/sec (40kHz). Thus, a voltage doubler
at high data rates saves even more power.
Auto-Shutdown—The Ideal RS-232 IC
Page 3 of 9
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件