Datasheet 搜索 > 8位微控制器 > Microchip(微芯) > PIC16C57C-20/SP 数据手册 > PIC16C57C-20/SP 开发手册 2/22 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 0.144
PIC16C57C-20/SP 开发手册 - Microchip(微芯)
制造商:
Microchip(微芯)
分类:
8位微控制器
封装:
SPDIP-28
描述:
MICROCHIP PIC16C57C-20/SP 微控制器, 8位, PIC16C5xx, 40 MHz, 3 KB, 72 Byte, 28 引脚, NDIP
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
页面导航:
技术参数、封装参数在P18
导航目录
PIC16C57C-20/SP数据手册
Page:
of 22 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
AN1066
DS01066B-page 2 © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
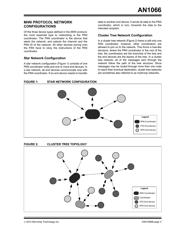
to other devices or applications. By using sockets,
nodes in the network can find communication partners
dynamically without having to know any information
about them.
MiWi PROTOCOL OVERVIEW
The MiWi protocol is based on the MAC and PHY
layers of the IEEE 802.15.4 specification, and is
tailored for simple network development in the 2.4 GHz
and subGHz ISM frequency bands. The protocol
provides the features to find, form and join a network,
as well as discovering nodes on the network and route
to them. It does not cover any application-specific
issues, such as how to select which network to join to,
how to decided when a link is broken or how often
devices should communicate.
IEEE 802.15.4 MAC
The MiWi protocol uses IEEE Standard 802.15.4 as
reference to develop its MAC layer.
Similar to IEEE 802.15.4, MiWi protocol uses an
Acknowledged data transfer mechanism in the MAC.
This method uses a special ACK flag in the packet
header. When this flag is set, Acknowledgement to the
transmitter by its receiver is required; this ensures that a
frame is, in fact, delivered. If the frame is transmitted with
an ACK flag set and the Acknowledgement is not
received within a certain time-out period, the transmitter
will retry the transmission for a fixed number of times
before declaring an error.
It is important to note that the reception of an
Acknowledgement simply indicates that a frame was
properly received by the MAC layer. However, it does not
indicate that the frame was processed correctly. It is
possible that the MAC layer of the receiving node
received and Acknowledged a frame correctly, but due
to the lack of processing resources, a frame might be
discarded by upper layers. As a result, the upper layers
of the application may require additional
Acknowledgement response.
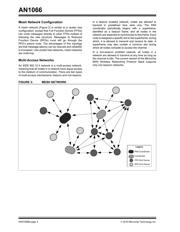
Device Types
IEEE 802.15.4 defines devices based on their overall
functionality. There are basically two device types as
shown in Table 1.
The MiWi protocol defines three types of MiWi protocol
devices, based on their functions in the network: PAN
Coordinator, Coordinator and End Device. The MiWi
Wireless Networking Protocol Stack functionality helps
to determine the type of IEEE functionality that the
device requires. The MiWi protocol device types and
their relationship to IEEE device types are shown in
Table 2.
TABLE 1: IEEE 802.15.4™ FUNCTIONAL DEVICE TYPES
TABLE 2: MiWi™ PROTOCOL DEVICE TYPES
Device Type Services Offered Typical Power Source
Typical Receiver Idle
Configuration
Full Function Device (FFD) All or Most Mains On
Reduced Function Device
(RFD)
Limited Battery Off
Device Type IEEE Device Type Typical Function
PAN Coordinator FFD One per network. Forms the network, allocates network
addresses, holds binding table.
Coordinator FFD Optional. Extends the physical range of the network. Allows
more nodes to join the network. May also perform monitoring
and/or control functions.
End Device FFD or RFD Performs monitoring and/or control functions.
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件