Datasheet 搜索 > 微控制器 > ST Microelectronics(意法半导体) > STM32F102C6T6ATR 数据手册 > STM32F102C6T6ATR 开发手册 5/10 页

¥ 11.181
STM32F102C6T6ATR 开发手册 - ST Microelectronics(意法半导体)
制造商:
ST Microelectronics(意法半导体)
分类:
微控制器
封装:
LQFP-48
描述:
STM32 系列 32 位 32 kB 闪存 6 kB RAM 基于 ARM 微控制器 - LQFP-48
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
页面导航:
应用领域在P10
导航目录
STM32F102C6T6ATR数据手册
Page:
of 10 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件

AN3109 FIFO emulation with DMA
Doc ID 16795 Rev 1 5/10
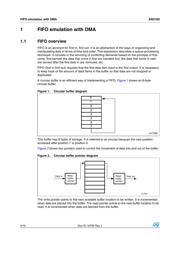
1.2 RAM FIFO emulation in STM32 microcontrollers
The DMA capability of STM32 microcontrollers greatly simplifies the FIFO implementation.
DMA is an efficient way of implementing RAM FIFO based on the principle described in
Section 1.1: FIFO overview.
DMA features that simplify the FIFO implementation:
● Independent source and destination transfer sizes (byte, half-word, word), to emulate
packing and unpacking
● Support for circular buffer management
● Access to Flash memory, SRAM, APB1, APB2 and AHB peripherals as source and
destination
● Programmable number of data items to be transferred: up to 65536
All these features concur to minimize the software overhead associated with data storage.
The DMA memory increment mode is very useful because, with it, the data pointer can be
automatically incremented.
Here, the DMA buffer emulates the FIFO buffer. The write buffer pointer (DMA pointer) is
automatically incremented and the DMA count is automatically decremented when the FIFO
is filled.
The read buffer locations are incremented by software every time data are retrieved from the
FIFO buffer.
1.3 FIFO software implementation
1.3.1 Implementation
This example describes the basic architecture of a circular buffer FIFO for a communication
peripheral. The USART is provided as an example.
Data are received and stored into the DMA circular buffer, where they remain until they are
removed and manipulated.
The transmitter transmits n data items using DMA. The message length (n) is known in
advance.
The receiver receives m (potentially unknown) data items using DMA. It is still possible to
get the peripheral’s RXNE interrupt even when using DMA. In fact, the interrupt from the
peripheral emulates the FIFO nonempty interrupt.
For reception:
● There is no need to clear the RXNE flag in the receive interrupt routine, as it was
automatically cleared by the DMA data read operation. However, the interrupt remains
pending in the NVIC (even though the RXNE flag is no longer set).
● Two buffers are used:
– RxBuffer2: it is defined as the DMA memory base address from which data will be
read. This buffer emulates the FIFO buffer.
– RxBuffer2_SW: it is a software buffer used, inside the receive interrupt routine, to
transfer the received data from the FIFO. It is the final data storage destination.
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件