Datasheet 搜索 > 运算放大器 > ADI(亚德诺) > ADA4084-1ARJZ-RL 数据手册 > ADA4084-1ARJZ-RL 其他数据使用手册 1/8 页

¥ 21.001
ADA4084-1ARJZ-RL 其他数据使用手册 - ADI(亚德诺)
制造商:
ADI(亚德诺)
分类:
运算放大器
封装:
SOT-23-5
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
ADA4084-1ARJZ-RL数据手册
Page:
of 8 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
AN-849
APPLICATION NOTE
One Technology Way • P.O. Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel: 781.329.4700 • Fax: 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
Rev. A | Page 1 of 8
Using Op Amps as Comparators
by James Bryant
INTRODUCTION
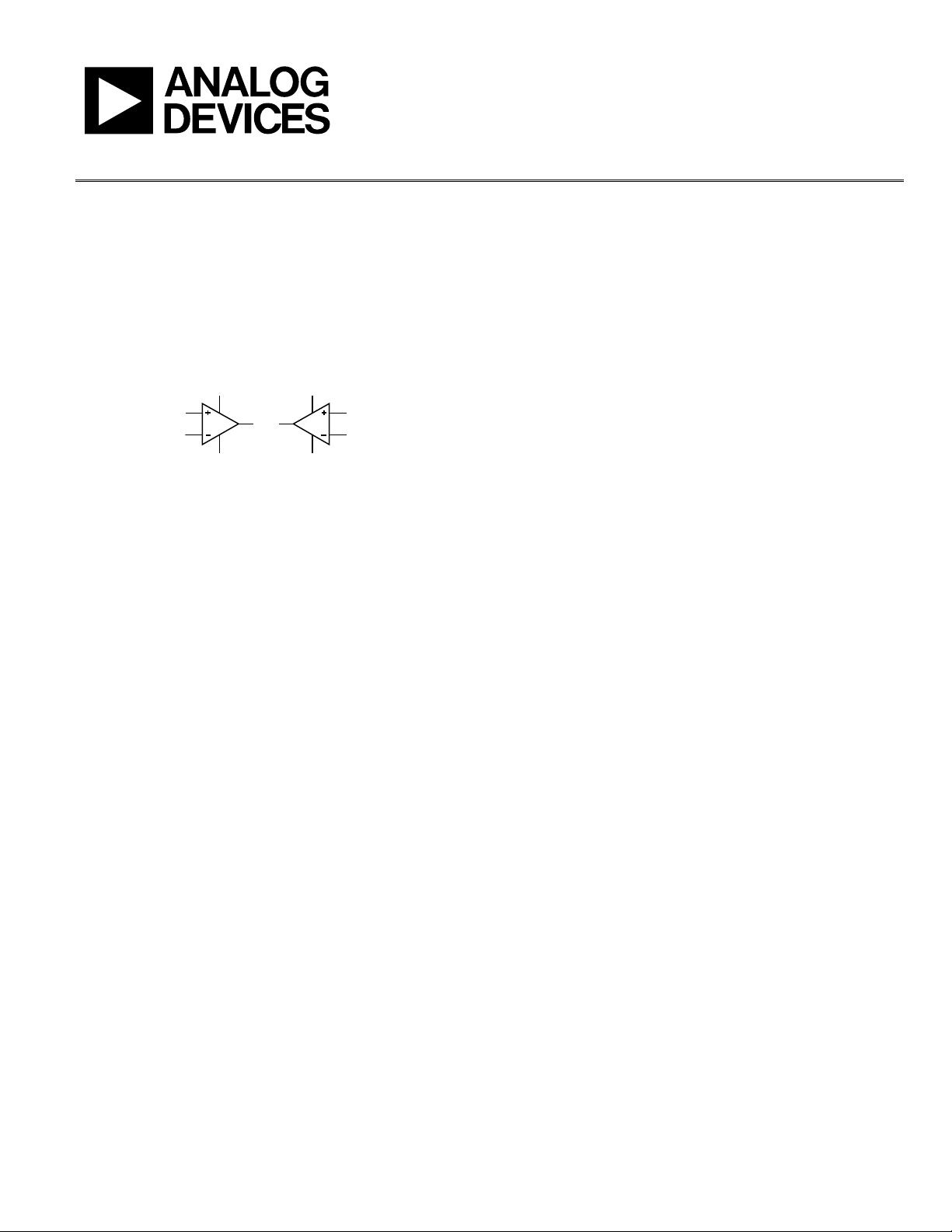
A comparator is a device with two input terminals, inverting
and noninverting, and an output that usually swings from rail to
rail. So is an op amp.
V+
V–
V+
V–
06125-001
Figure 1.
A comparator has low offset, high gain, and high common-mode
rejection. So does an op amp.
So what is the difference? A comparator has a logic output that
indicates which of the two inputs is at a higher potential. If its
output is TTL or CMOS compatible (and many comparators
are), it is always intended to be at one rail or the other—or
making a rapid transition between the two.
An op amp has an analog output that is not typically close to the
supply rails, but is somewhere between them. It is designed to
be used in closed-loop applications with feedback from its
output to its inverting input. But the outputs of most modern
op amps can swing close to their supply rails. Why not use them
as comparators?
Op amps have high gain, low offset, and high common-mode
rejection. They usually have lower bias current and are cheaper
than comparators. In addition, op amps are often available in
packages of two or four—if you need three op amps and a
comparator, it seems pointless to buy four op amps, not use one
of them, and then buy a separate comparator.
However, the best advice on using an op amp as comparator is
very simple—don’t!
Comparators are designed to work as open-loop systems, to
drive logic circuits, and to work at high speed, even when
overdriven. Op amps are designed for none of these. They are
intended to work as closed-loop systems, to drive simple
resistive or reactive loads, and should never be overdriven to
saturation.
But it is tempting to use op amps as comparators for a number
of reasons. The remainder of this document summarizes the
reasons and warns of possible unexpected consequences of
using an op amp as a comparator.
WHY USE AN OP AMP AS A COMPARATOR?
• Convenience
• Economy
• Low I
B
• Low V
OS
There are several reasons to use op amps as comparators. Some
are technical, one is purely economic. Op amps are manufactured
as single devices, but also as duals and quads, two or four op
amps on a single chip. These duals and quads are cheaper than
two or four separate op amps and occupy less board space, saving
yet more money. It is economical to use the spare op amp in a
quad as a comparator rather than buying an additional
comparator, but this is not a good design practice.
Comparators are designed for clean fast switching and, as a result,
often have worse dc parameters than many op amps. So it may be
convenient to use an op amp as a comparator in applications
requiring low V
OS
, low I
B
, and wide CMR. It is never worthwhile
to use an op amp as a comparator if high speed is important.
WHY NOT USE AN OP AMP AS A COMPARATOR?
• Speed
• Inconvenient input structures
• Inconvenient logic structures
• Stability/hysteresis
There are several reasons not to use op amps as comparators.
First and foremost is speed, but there are also output levels,
stability (and hysteresis), and a number of input structure
considerations. The following sections provide more detail.
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件