Datasheet 搜索 > 微控制器 > ATMEL(爱特美尔) > AT89C51AC3-SLSUM 数据手册 > AT89C51AC3-SLSUM 其他数据使用手册 1/16 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 7.213
AT89C51AC3-SLSUM 其他数据使用手册 - ATMEL(爱特美尔)
制造商:
ATMEL(爱特美尔)
分类:
微控制器
封装:
PLCC-44
描述:
AT89C51 系列 60 MHz 64 KB 闪存 2.25 KB SRAM 8 位 微控制器 - PLCC-44
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
AT89C51AC3-SLSUM数据手册
Page:
of 16 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
1
Analyzing the Behavior of an Oscillator and
Ensuring Good Start-up
This application note explains how an oscillator functions and which methods can be
used to check if the oscillation conditions are met in order to ensure a good start-up
when power is applied.
Oscillator Fundamentals
A microcontroller integrates on-chip an oscillator to generate a stable clock used to
synchronize the CPU and the peripherals.
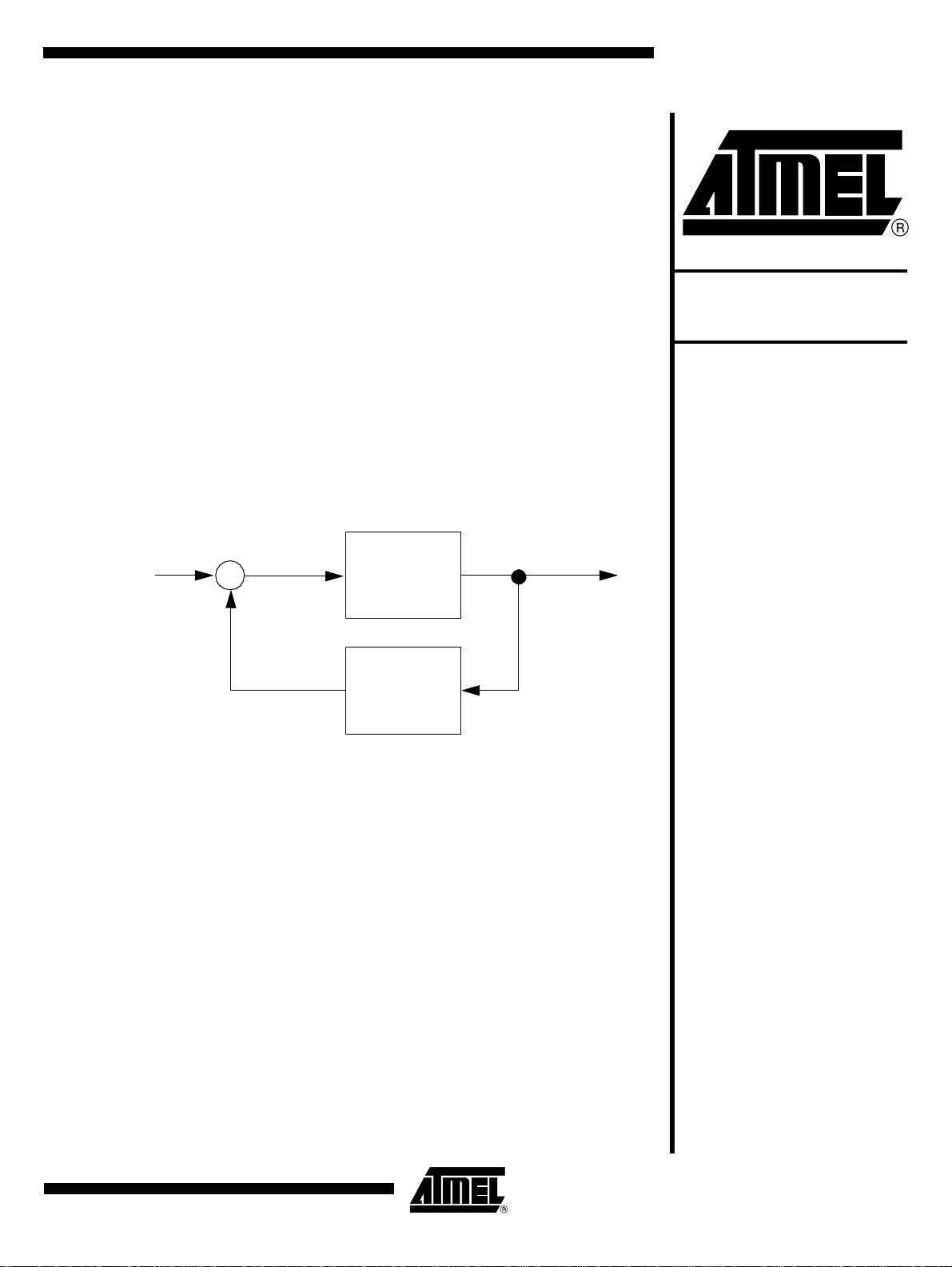
Figure 1. Basic Oscillator Architecture
The basic architecture of an oscillator (regardless of its structure) is shown in Figure 1
and built around an amplifier, a feed-back and noise applied on Xtal1 input. The role of
each elements is explained hereafter:
• Amplifier: Used to amplify the signal applied on Xtal1 and to lock the oscillations
exhibit Xtal2. The class A structure is the most popular but new ones are currently
used in order to optimize the consumption or other criterion,
• Feed-back loop: Used to filter the output signal and to send it to the Xtal1 input.
The oscillator stability is linked to the bandwidth of the loop. The narrower the
filter, the more stable the oscillator. Crystals or ceramic resonators are generally
used because they have the narrowest bandwidth and efficiency for the stability of
the frequency.
Amplifier
Feed-back
Loop
Noise
+
G(f)
H(f)
Xtal1
Xtal2
80C51 MCU’s
Application Note
Rev. 4363A–80C51–07/04
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件