Datasheet 搜索 > 电压基准芯片 > Maxim Integrated(美信) > MAX6126BASA21+ 数据手册 > MAX6126BASA21+ 其他数据使用手册 1/15 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 37.486
MAX6126BASA21+ 其他数据使用手册 - Maxim Integrated(美信)
制造商:
Maxim Integrated(美信)
分类:
电压基准芯片
封装:
SOIC-8
描述:
参考电压,1.2V 至 2.048V,Maxim Integrated### 电压参考,Maxim Integrated
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
页面导航:
技术参数、封装参数在P9P10P15
电气规格在P9
导航目录
MAX6126BASA21+数据手册
Page:
of 15 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件

Keywords: semiconductor noise, thermal noise, flicker, popcorn noise
TUTORIAL 5664
MANAGING NOISE IN THE SIGNAL CHAIN,
PART1: ANNOYING SEMICONDUCTOR NOISE,
PREVENTABLE OR INESCAPABLE?
Abstract: Generally speaking, noise is any electrical phenomenon that is unwelcomed in an electrical system.
This article is the first of a three-part series about noise in the signal chain. Here we focus on the internal
sources of noise found in all semiconductor devices: thermal, shot, avalanche, flicker, and popcorn noise. A
procedure to estimate noise voltage will be given along with an example. Finally, a free calculator is
presented that aids in estimating noise under conditions that are not specified in a device data sheet.
A similar version of this article appears on EDN, October 14, 2013.
Introduction
This is the first in a three-part series on managing noise in the signal chain. In this article we will focus on the
characteristics of semiconductor noise found in all ICs, explain how it is specified in device data sheets, and
show how to estimate the noise of a voltage reference under real-world conditions not specified in the data
sheet. In Part 2 we will focus on sources of noise and distortion particular to data converters and show how it
is specified in those data sheets. Our concluding Part 3 brings together Parts 1 and 2, and shows readers
how to optimize their noise budget and choose the most appropriate data converter for their application.
Understanding electrical noise is more important today than it has ever been. As 14- and 16-bit data
converters are becoming mainstream and 18- and 24-bit converters are increasingly available, noise is often
the single factor that limits a system’s performance. Clearly, understanding the origins and characteristics of
noise generated within an IC is key to achieving a system’s greatest possible accuracy.
Noise can irritate everyone, but it is especially annoying to analog design engineers. Generally speaking,
noise is any unwelcome electrical phenomenon in a signal chain. Depending on its origin, it may be classified
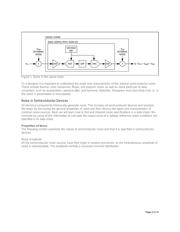
as external (interference) or internal (inherent). This is illustrated in the signal-chain diagram below (Figure
1
). All internal noise sources (V ) have been combined at the output and all external noise sources (V )
have been combined at the input to the signal chain.
int ext
Page 1 of 15
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件