Datasheet 搜索 > 8位微控制器 > Microchip(微芯) > PIC10F202-E/P 数据手册 > PIC10F202-E/P 产品描述及参数 1/54 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 5.615
PIC10F202-E/P 产品描述及参数 - Microchip(微芯)
制造商:
Microchip(微芯)
分类:
8位微控制器
封装:
PDIP-8
描述:
6引脚8位闪存微控制器 6-Pin, 8-Bit Flash Microcontrollers
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
页面导航:
原理图在P23
导航目录
PIC10F202-E/P数据手册
Page:
of 54 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
© 2009 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51292R-page 1
Header Board Specification
WHY DO I NEED A HEADER TO DEBUG?
Some PIC
®
microcontrollers, particularly low pin count devices (with 20 pins or less),
generally must use a header for debugging. This is done to free up I/O lines for your
application and to make production parts more affordable. Optional headers are also
available for high pin count devices (with 64 pins or higher).
Debugging requires a two-line connection (plus V
DD, VSS and VPP) to communicate
with the device. In a high pin count device, losing a few I/O lines is generally not a prob-
lem for most designs. But in a low pin count device, it can be a critical problem. Imagine
having to do an 8-pin design where there are only 5 I/Os, having used up 2 I/Os just for
debugging!
Headers are also used to save you money. In high pin count devices, adding debug-
ging to the silicon can generally be done at little or no cost since the silicon is already
fairly large. However, low pin count devices are low cost specifically because they use
very little silicon. So, adding debugging circuitry on-board these parts would add sig-
nificant cost since it would raise the amount of silicon used by a considerable percent-
age. The header places the cost for debugging up front and frees your production parts
from the extra cost of an unused debug module.
Microchip also makes optional debug modules, usually for high pin count devices. The
module is optional because you can still do basic debugging without a header, but if
you use one, you get back I/O lines, and may also gain additional debugging features.
Only certain devices can use an optional header, see the device page on our website
for details.
Microchip lists what header must be ordered to work with your device, if one is required.
Simply consult the device page on our website, or our other ordering guides.
Note that in all cases, devices can be programmed “in circuit” (called ICSP™) with very
few exceptions. Even devices without an internal debug feature can still be pro-
grammed by connecting the programming/debugging tool to the in-circuit programming
lines. These devices simply cannot perform debugging without a header.
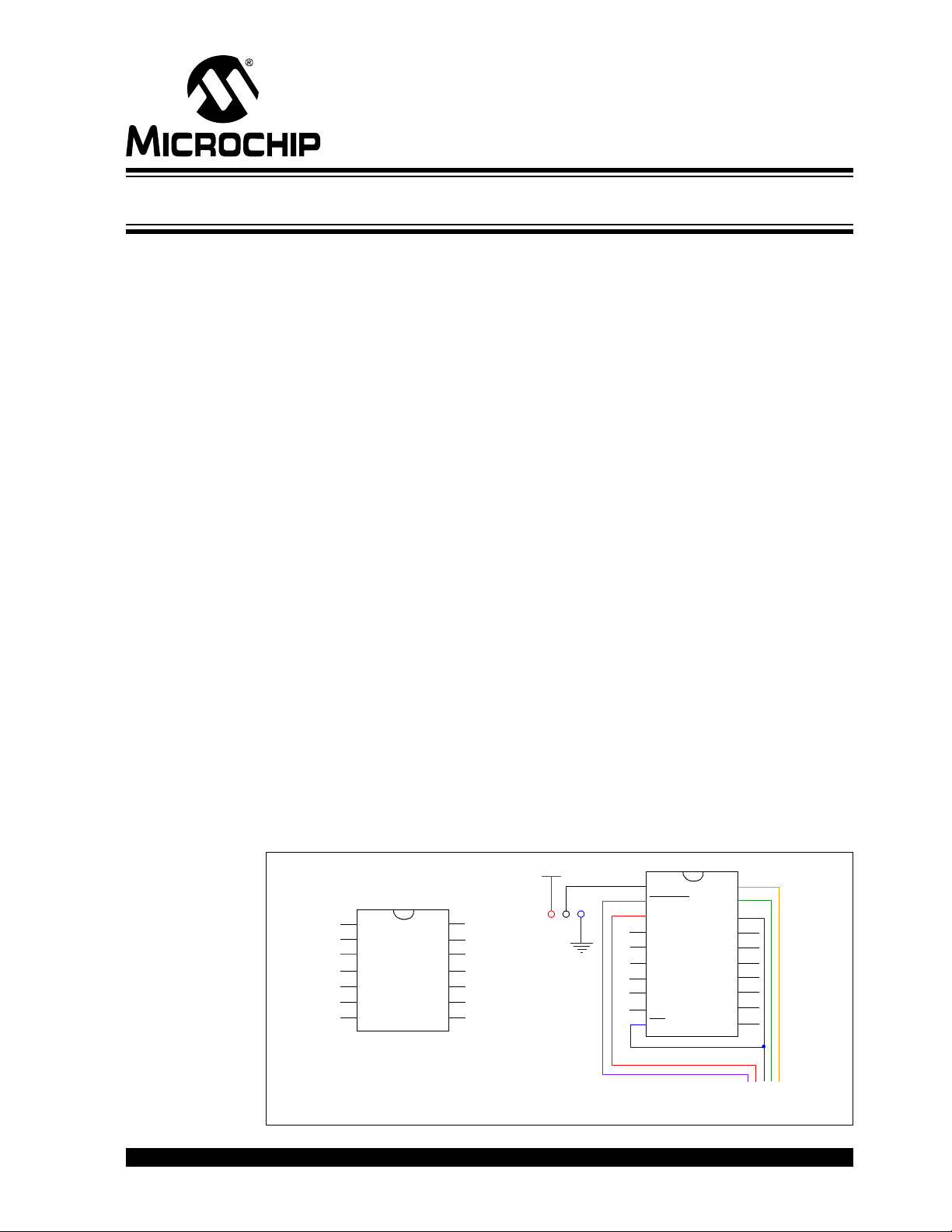
FIGURE 1: PRODUCTION DEVICE VS. HEADER DEVICE (-ICE/-ICD)
ENABLE
ICDMCLR
V
DD
ICDCLK
ICDDATA
Vss
ICD
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
JP1
2
1
3
V
DD
To Tool Connector
8
9
10
11
12
13
-ICE/-ICD Device
V
DD
Vss
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
on Header Board
Production Device
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件