Datasheet 搜索 > 微处理器 > NXP(恩智浦) > MCIMX6S5EVM10ACR 数据手册 > MCIMX6S5EVM10ACR 用户编程技术手册 4/22 页
¥ 239.436
MCIMX6S5EVM10ACR 用户编程技术手册 - NXP(恩智浦)
制造商:
NXP(恩智浦)
分类:
微处理器
封装:
BGA-624
描述:
微处理器, i.MX 6 Solo系列, 32位, 1GHz, 1.35V至1.5V, MAPBGA-624
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
MCIMX6S5EVM10ACR数据手册
Page:
of 22 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
SRK Revocation on i.MX 6 Series
Secure Boot on i.MX50, i.MX53, and i.MX 6 Series using HABv4, Rev. 1, 10/2015
4 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2. Overview
HAB authentication is based on public key cryptography using the RSA algorithm in which image data
is signed offline using a series of private keys. The resulting signed image data is then verified on the
i.MX processor using the corresponding public keys. This key structure is known as a PKI tree. Super
Root Keys, or SRK, are components of the PKI tree. HAB relies on a table of the public SRKs to be
hashed and placed in fuses on the target. The Freescale Code Signing Tool, CST, is used in this guide to
generate the HABv4 signatures for images using the PKI tree data and SRK table. On the target, HAB
evaluates the SRK table included in the signature by hashing it and comparing the result to the SRK fuse
values. If the SRK verification is successful, this establishes the root of trust, and the remainder of the
signature can be processed to authenticate the image. Detailed information for CST and HAB can be
found in their respective user guides included in the CST package.
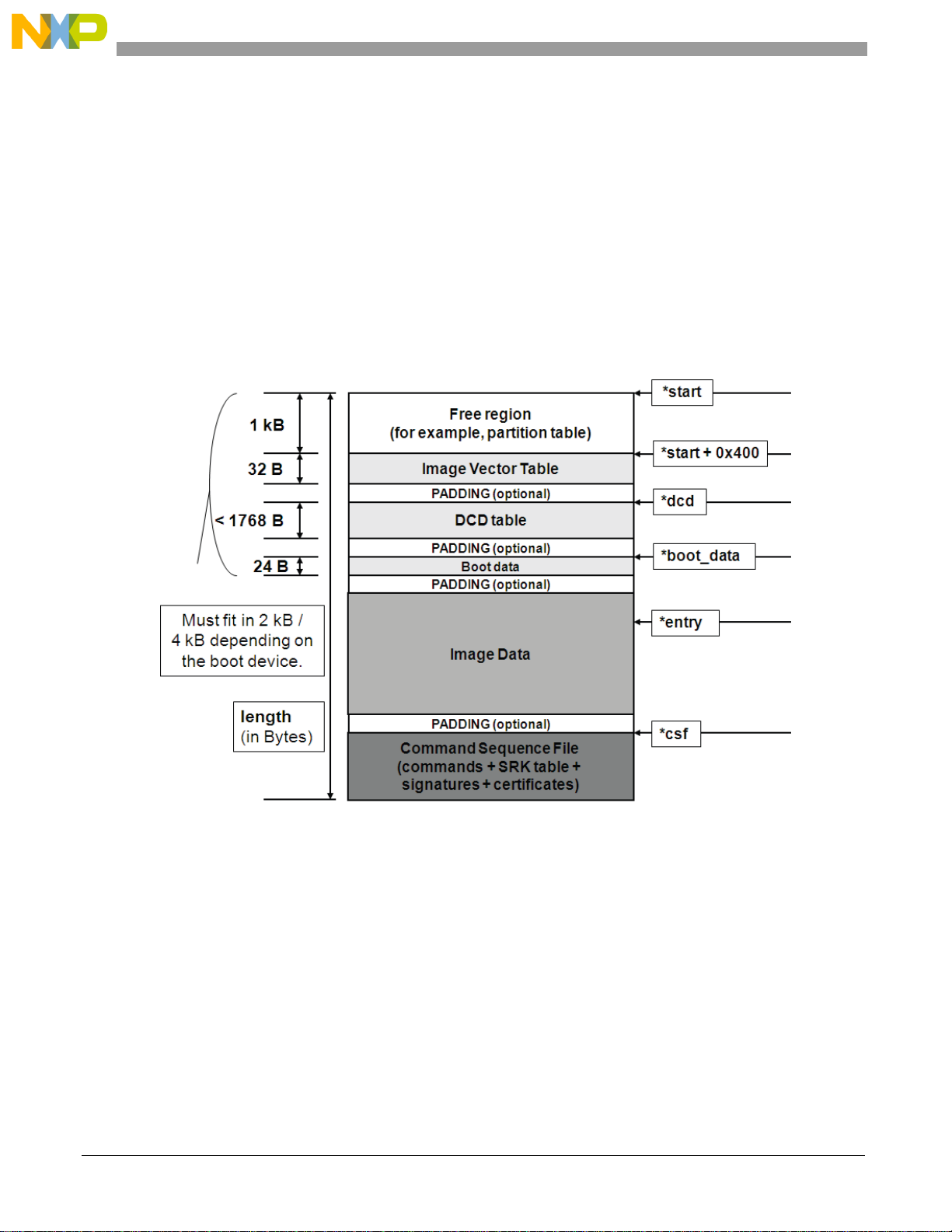
Figure 1. Typical memory layout of a signed image
NOTE
HAB requires that the IVT, initial bye of boot data, DCD table, and first
word of the image must all be covered by a digital signature.
3. Code signing example
The following sections detail the step by step process to securely boot an i.MX 6 Series part with
HABv4. After completing the steps, the image will have a valid HABv4 signature attached and the part
will be “closed”. Once “closed”, the part will only execute signed images.
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件







