Datasheet 搜索 > 接口芯片 > Maxim Integrated(美信) > MAX4051AEEE+T 数据手册 > MAX4051AEEE+T 其他数据使用手册 6/17 页

 器件3D模型
器件3D模型¥ 25.779
MAX4051AEEE+T 其他数据使用手册 - Maxim Integrated(美信)
制造商:
Maxim Integrated(美信)
分类:
接口芯片
封装:
SSOP-16
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
页面导航:
应用领域在P4P8
导航目录
MAX4051AEEE+T数据手册
Page:
of 17 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件
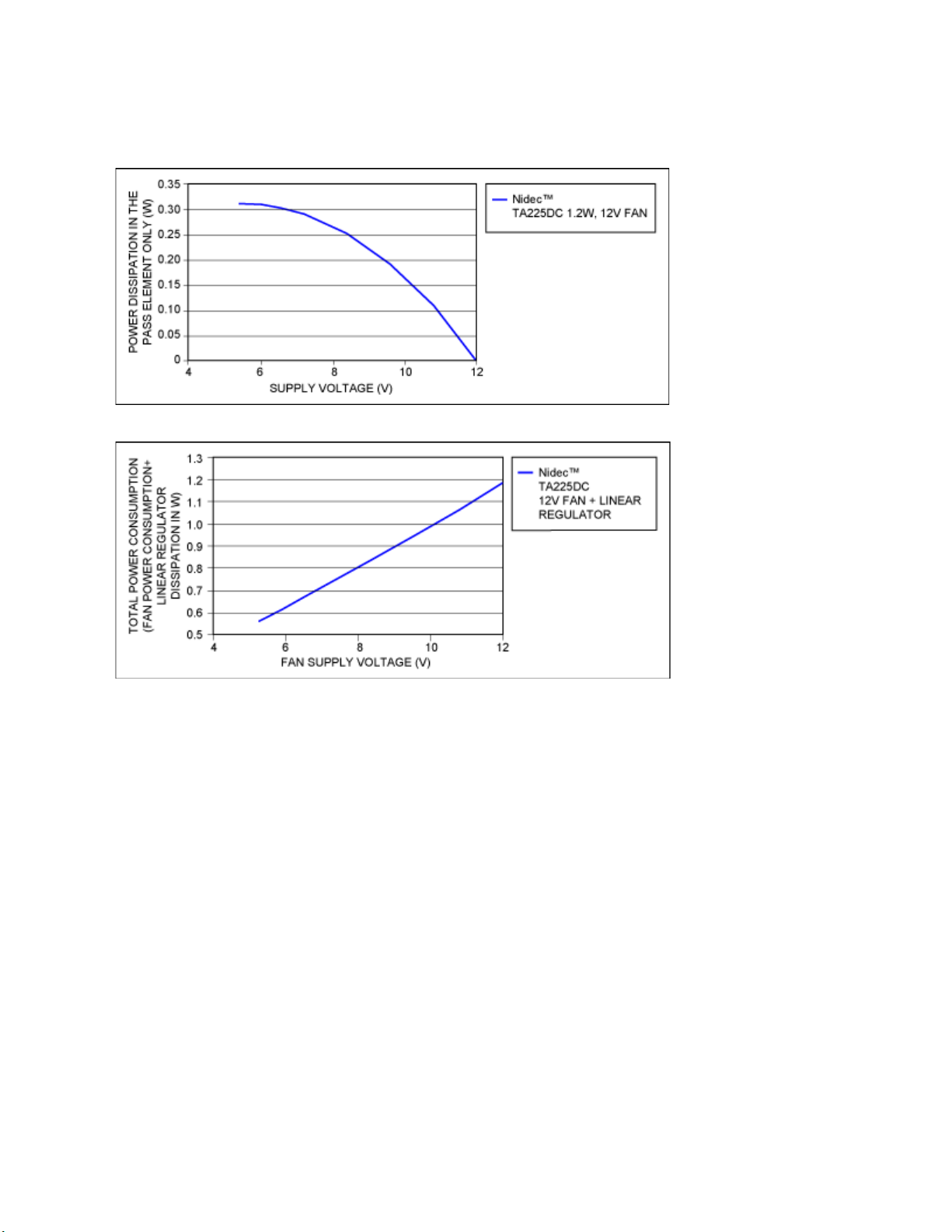
though a power-dissipating device is being used, there is still an overall power savings when fan speed
is reduced. See Figure 6.
Figure 5. Power dissipation in a linear-regulator pass element versus fan supply voltage.
Figure 6. Total power consumption of a linearly regulated fan circuit.
Startup and stall issues are related. Fans require a certain voltage before they will start. This is called
"startup voltage." Once a fan is already spinning, decreasing the voltage below the stall voltage will
cause the fan to stop. The startup voltage is equal to or (usually) greater than the stall voltage. Typically
they are 25% to 50% of the rated voltage for the fan. When linear regulation is used without speed
monitoring, there is no way of knowing if a fan has stalled or even started.
There are several solutions to this problem. One is to prevent voltages across the fan from going lower
than the startup voltage. Although this is easily accomplished in software, selecting the correct voltage to
ensure proper startup for all fans and accounting for aging can limit the useful range of speed control.
You might have to choose a minimum worst-case voltage of 60% nominal to make sure all fans will start.
This can be wasteful, considering that the average fan might easily be controlled down to 40%. Another
solution is to use a fan with a tachometer. The tachometer can now be monitored by a microcontroller,
allowing software to know when a fan has not started or if it has stalled. Although this method is
significantly more robust and less wasteful, it requires design time and additional hardware/software
resources.
DC-DC Regulation
DC-DC regulation is similar to linear regulation in that it controls the speed of the fan by adjusting the
DC voltage across it. However, unlike a linear regulator, a DC-DC regulator uses a switch-mode power
Page 6 of 17
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件